Astonishing Michelin Tyres — A Practical Guide to the Brand, Technology and Selection
From everyday commuting to performance driving and long‑distance touring, Michelin’s tyre portfolio spans many needs. This guide explains the brand’s background, core technologies, performance traits across conditions, and how to read sizes and codes so you can choose and maintain the right set with confidence in your area.
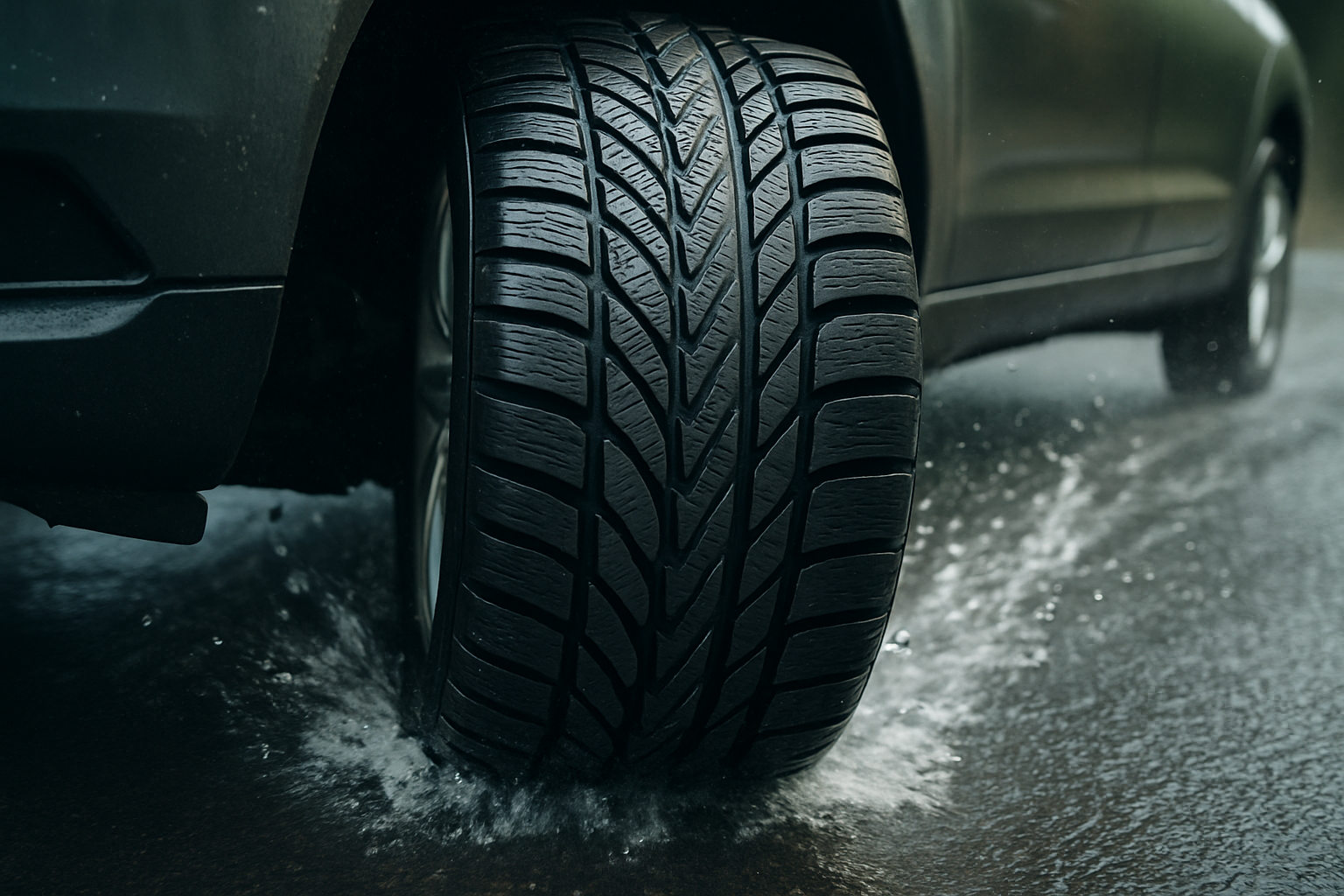

Tyres are the only contact points between a vehicle and the road, so understanding what differentiates a brand’s design, materials, and testing approach matters. Michelin has built a reputation around longevity, safety, and consistent performance, but its range is broad and the technical terms can be confusing. Below, we break down the brand’s history and sustainability efforts, the technologies used in modern Michelin tyres, how they perform in varying conditions, what affects durability and safety, and how to select the right size and specification for your vehicle.
Michelin at a glance: history, reputation, sustainability
Founded in France in 1889, Michelin has influenced road mobility for well over a century, from the first removable pneumatic tyres to innovations for aviation, cycling, and motorsport. Its reputation today rests on a blend of long tread life, strong wet‑weather grip in key lines, and extensive testing. Sustainability has moved center stage in recent years: Michelin targets increased use of recycled and renewable materials, reduced rolling resistance to lower fuel or energy consumption, and factory programs that cut emissions and waste. The company also participates in end‑of‑life tyre collection and supports circular initiatives where available, aiming to improve both performance and environmental impact over a tyre’s lifespan.
Core technologies and innovations behind Michelin tyres
Across passenger, SUV, and light‑truck segments, Michelin uses compound chemistry and carcass design to balance grip, comfort, and wear. Silica‑rich tread compounds help improve wet braking and rolling resistance, while reinforced bead and belt packages maintain stability at speed. 3D sipes (fine slits in tread blocks) support winter grip by creating biting edges without overly softening the tread. Directional or V‑shaped patterns in lines like CrossClimate aid water evacuation and snow traction, and shoulder block stiffness is tuned to boost cornering. Some touring products are designed to maintain performance as they wear, with evolving grooves that widen as tread depth decreases. Noise‑reduction features, such as pitch sequencing and foam in select fitments, aim to lower cabin sound.
Performance: wet, dry, winter and off‑road handling
Performance varies by line and size, but patterns emerge. Summer and ultra‑high‑performance (UHP) models prioritize dry grip and steering precision, with compounds meant to stay stable at higher temperatures. Touring all‑season tyres focus on balanced everyday use, emphasizing wet braking, hydroplaning resistance, and ride comfort. “All‑weather” tyres with winter certification (3PMSF symbol) like the CrossClimate family are tuned to handle cold, slush, and moderate snow better than typical all‑seasons, though they are not a replacement for dedicated winter tyres in severe conditions. For snow‑belt regions or mountain routes, winter tyres with specialized siping and softer cold‑temperature compounds deliver shorter stopping distances and improved traction. Light‑truck and SUV lines with off‑road intent add cut‑ and chip‑resistant rubber, stone ejectors, and more robust sidewalls to cope with gravel and occasional trails, trading some on‑road quietness for durability.
Durability, safety considerations and maintenance tips
Longevity depends on compound, driving style, climate, and vehicle setup. To support durability, maintain correct inflation pressures (including for heavy loads), rotate at the intervals recommended by your vehicle maker, and ensure wheel alignment is in spec to prevent shoulder wear. For safety, check tread depth with a gauge; many jurisdictions consider 1.6 mm (2/32 in) the legal minimum, but wet braking often degrades well before that. Inspect for cuts, bulges, embedded objects, or sidewall damage. Replace tyres older than about six to ten years regardless of tread depth due to compound aging; the DOT code on the sidewall shows the week and year of manufacture. In EVs, expect faster wear from higher torque and weight; selecting tyres labeled for EV use may reduce rolling resistance and help range while maintaining load capacity.
Choosing the right tyre: sizes, codes, buying advice
Start with the vehicle owner’s manual or the driver‑door placard for the recommended size, load index, and speed rating. A size like 225/45R17 94Y reads as: 225 mm width, 45% aspect ratio, radial construction, 17‑inch wheel, load index 94, speed rating Y. Match or exceed the load index and speed symbol specified by the manufacturer. Consider your climate and driving: warm‑weather performance, balanced all‑season touring, winter‑certified all‑weather, or dedicated winter. For SUVs and trucks, check whether you need highway‑terrain, all‑terrain, or commercial‑grade fitments. Evaluate rolling resistance if fuel efficiency or EV range matters. When purchasing, compare verified test results and labeling for wet grip, noise, and efficiency. Professional installation by local services ensures proper mounting, balancing, and TPMS handling, and many retailers offer road‑hazard coverage that can be valuable for long commutes.
Popular Michelin lines compared
Below is a high‑level look at representative Michelin ranges to illustrate typical use cases and features. Availability varies by region and size.
| Product/Service Name | Provider | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Pilot Sport 5 (UHP summer) | Michelin | Dry and wet grip focus, precise steering, reinforced casing for sporty driving |
| Primacy 4+ (touring) | Michelin | Emphasis on wet braking as tyres wear, quiet ride, efficiency‑minded compound |
| CrossClimate 2 (all‑weather, 3PMSF) | Michelin | V‑shaped tread for water and slush, winter certification, year‑round versatility |
| LTX Trail (SUV/light truck) | Michelin | On‑road comfort with light off‑road durability, cut‑resistant tread, stone ejectors |
| Agilis CrossClimate (van/commercial) | Michelin | Robust sidewalls, high load ratings, 3PMSF traction for delivery use |
Practical upkeep: storage, repairs, and replacements
Store tyres in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and solvents; if on rims, reduce and mark pressures before stacking. For punctures, only consider repairs in the crown area and within size limits using a plug‑patch method; sidewall damage is not repairable. Replace tyres in axle pairs on vehicles without staggered fitments to maintain balance, and on AWD models follow maker guidance to avoid drivetrain stress. Recheck torque on lug nuts after installation if recommended by your installer, and verify TPMS readings after any pressure changes.
Conclusion
Selecting Michelin tyres comes down to matching your climate, vehicle requirements, and driving style with the correct line, size, and ratings. Understanding the brand’s material science, tread designs, and testing priorities helps interpret labels and reviews, while consistent maintenance protects both safety and investment over the long term.