Electric Bass Boats: A Practical Guide to Choosing, Using, and Maintaining Electric-Powered Bass Fishing Boats
Electric bass boats represent a significant shift in fishing technology, combining environmental consciousness with practical angling capabilities. These vessels utilize advanced electric propulsion systems to deliver quiet operation, reduced maintenance requirements, and zero emissions on the water. As battery technology continues to improve and charging infrastructure expands, electric bass boats are becoming increasingly viable alternatives to traditional gas-powered models for serious anglers.
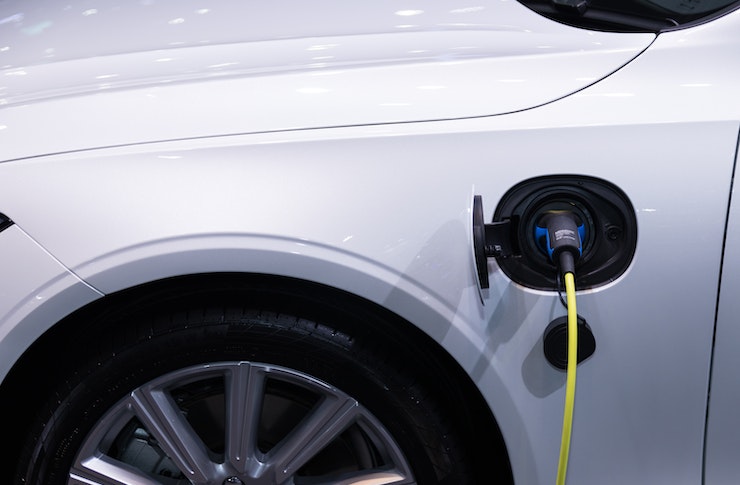

Modern electric bass boats have evolved from experimental concepts into sophisticated fishing platforms that rival their gas-powered counterparts in many aspects. The transition to electric propulsion brings unique advantages including whisper-quiet operation that won’t spook fish, instant torque delivery, and significantly reduced operating costs over time.
How Electric Bass Boats Work: Motors, Batteries, and Power Management
Electric bass boats operate through integrated systems combining high-capacity lithium batteries, efficient electric motors, and sophisticated power management controllers. The propulsion system typically features brushless DC motors that convert electrical energy directly into rotational force, eliminating the need for complex transmissions or gear systems found in traditional outboards.
Battery banks usually consist of lithium iron phosphate cells configured in series to achieve the required voltage, commonly ranging from 48V to 72V systems. Advanced battery management systems monitor individual cell temperatures, voltages, and current draw to optimize performance and prevent damage. Power distribution panels allow operators to allocate electrical resources between propulsion, electronics, and auxiliary systems based on fishing conditions and priorities.
Performance and Range: Speed, Endurance, and Real-World Expectations
Electric bass boats typically achieve top speeds between 25-45 mph depending on hull design, motor configuration, and battery capacity. While this may seem modest compared to high-performance gas boats, the instant torque delivery provides excellent acceleration and precise speed control crucial for fishing applications.
Range varies significantly based on operating conditions, with most electric bass boats capable of 4-8 hours of mixed-use fishing including trolling, positioning, and moderate-speed running. Trolling speeds of 2-5 mph can extend operating time to 10-12 hours, making electric boats particularly suitable for techniques requiring extended periods of slow-speed maneuvering.
Real-world performance depends heavily on factors including water temperature, wind conditions, boat loading, and operator habits. Cold weather can reduce battery capacity by 20-30%, while aggressive acceleration and high-speed operation significantly impact range.
Fishing Features and Layout: Decks, Storage, Electronics, and Trolling
Electric bass boats often feature optimized layouts that take advantage of the compact electric drivetrain. The absence of fuel tanks and complex engine compartments allows for increased storage capacity and more flexible deck configurations. Many models incorporate dedicated battery compartments with integrated cooling and monitoring systems.
Trolling capabilities represent a significant advantage of electric propulsion, with precise speed control and silent operation allowing anglers to work structure and cover without disturbing fish. Variable speed controls enable micro-adjustments impossible with traditional gas engines, particularly beneficial for techniques requiring specific presentation speeds.
Electronics integration is typically more straightforward in electric boats, with stable DC power systems providing clean electrical environments for sensitive fish finders, GPS units, and communication equipment. Some manufacturers offer integrated charging systems that can power electronics while simultaneously charging the propulsion batteries.
| Boat Model | Manufacturer | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bass Tracker Heritage | Tracker Marine | 16ft, 20hp electric, 8-hour range | $25,000-$30,000 |
| Alumacraft Competitor | Alumacraft | 18ft, dual motor setup, tournament features | $35,000-$42,000 |
| Lund Adventure | Lund Boats | 17ft, integrated electronics, premium finish | $38,000-$45,000 |
| Crestliner VT19 | Crestliner | 19ft, high-capacity batteries, professional layout | $42,000-$52,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Charging, Maintenance, and Battery Care
Charging infrastructure varies from standard 110V household outlets for overnight charging to high-capacity 240V systems that can replenish batteries in 2-4 hours. Many marinas are beginning to install dedicated charging stations, though availability remains limited compared to fuel docks.
Maintenance requirements for electric bass boats are generally minimal compared to gas-powered alternatives. Electric motors have fewer moving parts and require no oil changes, spark plug replacements, or fuel system servicing. However, proper battery care becomes critical for long-term performance and cost management.
Battery maintenance involves regular monitoring of charge levels, avoiding deep discharge cycles, and maintaining proper storage temperatures. Most lithium systems include built-in protection circuits, but understanding proper charging protocols and storage procedures can significantly extend battery life and maintain performance.
Buying Considerations and Safety Tips
Potential buyers should carefully evaluate their fishing patterns, typical outing duration, and access to charging infrastructure before committing to electric propulsion. Range anxiety remains a legitimate concern, particularly for anglers who frequently fish large bodies of water or participate in tournaments requiring extended travel distances.
Safety considerations include understanding battery system limitations, carrying appropriate emergency equipment, and developing contingency plans for power system failures. Unlike gas boats where fuel can be transferred from other vessels, electric boats require different emergency protocols and backup systems.
Warranty coverage varies significantly between manufacturers, with battery warranties typically ranging from 3-8 years depending on usage patterns and maintenance compliance. Understanding warranty terms and local service availability becomes crucial given the specialized nature of electric marine systems.
Electric bass boats represent a compelling option for anglers prioritizing quiet operation, environmental responsibility, and reduced operating costs. While range limitations and charging infrastructure challenges remain, advancing technology continues to address these concerns, making electric propulsion increasingly viable for serious bass fishing applications.