Mobil Scooter — Essential Guide to Choosing, Using, and Maintaining the Product
Mobility scooters and electric scooters have transformed personal transportation, offering convenient solutions for daily commutes, recreational rides, and enhanced independence. Whether you're considering a compact e-scooter for urban travel or a robust mobility scooter for accessibility needs, understanding the available options, features, and maintenance requirements is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental aspects of scooters, helping you make informed decisions about selection, operation, safety compliance, and long-term care to maximize your investment and riding experience.
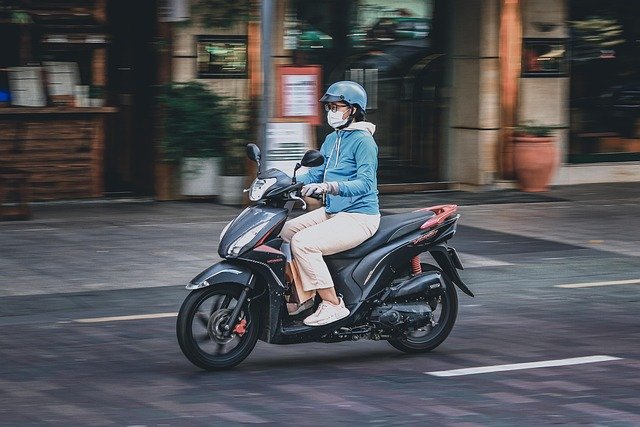

Mobility and electric scooters represent a diverse category of personal transportation devices designed to meet various needs, from enhancing independence for individuals with mobility challenges to providing eco-friendly urban commuting solutions. The market offers numerous models with varying specifications, making it essential to understand what distinguishes different types and how to select, operate, and maintain these vehicles effectively.
Understanding the Mobil Scooter: types, core components, and key features
Scooters fall into two primary categories: mobility scooters designed for individuals with limited mobility, and electric scooters (e-scooters) intended for general transportation. Mobility scooters typically feature three or four wheels, a comfortable seat, handlebars or tiller steering, and electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. They prioritize stability, comfort, and ease of use for individuals who cannot walk long distances.
Electric scooters, by contrast, are standing platforms with two wheels, a handlebar for steering and control, and compact electric motors. They emphasize portability, speed, and maneuverability for urban environments. Core components shared across both types include the battery system (usually lithium-ion), motor (brushless DC motors are common), controller unit, braking system (disc, drum, or regenerative), and display panel showing speed, battery level, and distance traveled.
Key features vary significantly between models. Range typically spans from 15 to 40 kilometers per charge for e-scooters, while mobility scooters may achieve 20 to 50 kilometers depending on battery capacity. Motor power ranges from 250 watts for basic models to over 500 watts for performance-oriented designs. Additional features include suspension systems for smoother rides, LED lighting for visibility, water resistance ratings, and smart connectivity options allowing riders to track performance metrics through mobile applications.
Choosing the right model: range, weight capacity, size, and terrain suitability
Selecting an appropriate scooter requires careful consideration of several factors aligned with your specific needs and usage patterns. Range is critical—evaluate your typical travel distances and choose a model offering at least 20 percent more range than your daily requirements to account for battery degradation over time and varying terrain conditions.
Weight capacity is equally important. Most e-scooters support riders between 100 and 120 kilograms, while mobility scooters often accommodate 135 to 180 kilograms or more. Exceeding weight limits compromises safety, performance, and component longevity. Size considerations include both the scooter dimensions and portability requirements. Foldable e-scooters weighing 10 to 15 kilograms suit users needing to carry their device on public transportation or store it in compact spaces. Mobility scooters, being larger and heavier (40 to 80 kilograms), require adequate storage and may need vehicle lifts for transport.
Terrain suitability depends on wheel size, suspension quality, and motor power. Small wheels (15 to 20 centimeters) work well on smooth pavement but struggle with uneven surfaces. Larger wheels (25 centimeters or more) with pneumatic tires and suspension systems handle rougher terrain, inclines, and outdoor environments more effectively. Consider where you will primarily ride—urban sidewalks, bike paths, indoor spaces, or varied outdoor terrain—and match specifications accordingly.
Safety, controls, and complying with local regulations
Safe operation begins with understanding your scooter’s control system. Most e-scooters feature thumb or trigger throttles for acceleration, hand brakes (lever-operated disc or drum brakes), and sometimes foot-activated rear brakes. Mobility scooters use tiller controls with speed adjustment dials, direction indicators, and ergonomic hand grips. Familiarize yourself thoroughly with all controls before riding in traffic or crowded areas.
Safety equipment is essential. Helmets significantly reduce head injury risk and are mandatory in many jurisdictions for e-scooter riders. Reflective clothing, lights, and bells enhance visibility and communication with pedestrians and vehicles. Regular brake testing, tire pressure checks, and ensuring all fasteners are secure prevent mechanical failures during operation.
Regulations vary considerably by location. Many regions classify e-scooters as personal mobility devices subject to specific rules regarding maximum speed (often 25 kilometers per hour), where riding is permitted (bike lanes versus sidewalks), age restrictions, and licensing requirements. Some areas prohibit e-scooters entirely or restrict them to private property. Mobility scooters typically face fewer restrictions but may have designated access areas in public spaces. Research local laws thoroughly and maintain compliance to avoid fines and ensure safe, legal operation.
Routine maintenance, battery care, and common troubleshooting
Proper maintenance extends scooter lifespan and ensures reliable performance. Routine tasks include cleaning the frame and components to prevent dirt accumulation, inspecting tires for wear and maintaining proper pressure (typically 35 to 50 PSI for pneumatic tires), checking brake responsiveness and adjusting as needed, and tightening bolts and fasteners that may loosen with vibration over time.
Battery care is paramount for longevity and performance. Lithium-ion batteries, standard in modern scooters, perform best when kept between 20 and 80 percent charge rather than fully depleting or constantly charging to 100 percent. Store scooters in temperature-controlled environments, as extreme heat or cold degrades battery capacity. If storing long-term, charge to approximately 50 percent and recharge every two to three months to prevent deep discharge damage. Most batteries retain 70 to 80 percent capacity after 300 to 500 charge cycles, equating to two to four years of typical use.
Common troubleshooting issues include reduced range (often battery degradation or tire pressure problems), unresponsive controls (check connections and controller settings), unusual noises (inspect bearings, brakes, and motor mounts), and charging difficulties (examine charger functionality and port cleanliness). Many problems resolve with simple adjustments, but persistent issues warrant professional service to prevent safety hazards or further damage.
Accessories, comfort options, transport and storage tips
Enhancing your scooter experience often involves accessories and modifications tailored to your usage patterns. Popular additions include phone mounts for navigation, additional lighting for improved visibility, upgraded seats or grips for comfort during longer rides, and cargo attachments like baskets or bags for carrying personal items. Suspension upgrades and larger tires can significantly improve ride quality on rough surfaces.
Comfort options are particularly important for mobility scooter users who spend extended periods seated. Cushioned seats with adjustable backrests, armrests, and swivel functions enhance usability. For e-scooters, ergonomic grips and wider decks reduce fatigue during standing rides. Weather protection accessories such as canopies or windshields benefit mobility scooter users in variable climates.
Transport considerations depend on scooter type and size. Foldable e-scooters simplify carrying and storage, fitting in car trunks or under desks. Mobility scooters require vehicle lifts, ramps, or disassembly into manageable components for transport. Storage should protect scooters from weather exposure, theft, and temperature extremes. Indoor storage is ideal, but covered outdoor areas with security measures work when indoor space is unavailable. Remove batteries for separate storage if leaving scooters unused for extended periods, and cover them to prevent dust accumulation and UV damage to plastic components.
Selecting, operating, and maintaining a mobility or electric scooter involves understanding technical specifications, matching features to your needs, prioritizing safety and legal compliance, and committing to regular care routines. With proper attention to these factors, scooters provide reliable, enjoyable transportation solutions that enhance independence and mobility for diverse users across various environments and applications.