Safe, Effective Earwax Removal: Methods, Products, and When to Seek Help
Earwax buildup can cause discomfort, hearing difficulties, and irritation, but removing it safely requires the right approach. While earwax serves important protective functions, excessive accumulation can lead to blockages that affect your daily life. Understanding proper removal methods, from gentle home remedies to professional treatments, helps you address earwax issues effectively while protecting your hearing health.
Earwax, medically known as cerumen, plays a crucial role in ear health by trapping dust, debris, and bacteria while naturally migrating out of the ear canal. However, when this natural process becomes disrupted, earwax can accumulate and create uncomfortable blockages that require careful attention.
Understanding earwax: purpose, symptoms of impaction, and when removal is needed
Earwax serves as your ear’s natural defense system, containing antimicrobial properties that protect against infections. The waxy substance typically moves outward naturally through jaw movements like chewing and talking. Problems arise when earwax becomes impacted, often due to narrow ear canals, excessive production, or improper cleaning attempts with cotton swabs that push wax deeper.
Symptoms of earwax impaction include hearing loss, ear fullness, tinnitus (ringing), dizziness, and earache. You may also experience itching or discharge. These symptoms indicate that professional evaluation or careful removal methods may be necessary.
At-home methods: ear drops, gentle irrigation, and safe tool use
Several safe home remedies can help soften and remove excess earwax. Mineral oil, baby oil, or glycerin drops applied daily for several days can soften hardened wax. Warm water irrigation using a rubber bulb syringe provides gentle pressure to flush out loosened material.
Avoid cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other objects that can push wax deeper or damage delicate ear structures. Instead, clean only the outer ear with a washcloth. If home methods don’t provide relief within a week, consider professional assistance.
Over-the-counter options: choosing drops, sprays, and kits responsibly
Pharmacies offer various earwax removal products, including carbamide peroxide drops, saline solutions, and complete removal kits. These products work by softening wax or providing controlled irrigation systems. Always read instructions carefully and discontinue use if you experience pain, dizziness, or worsening symptoms.
Some popular options include hydrogen peroxide-based drops that create bubbling action to break down wax, and specialized irrigation kits with controlled pressure systems. Choose products from reputable manufacturers and consult pharmacists about proper usage.
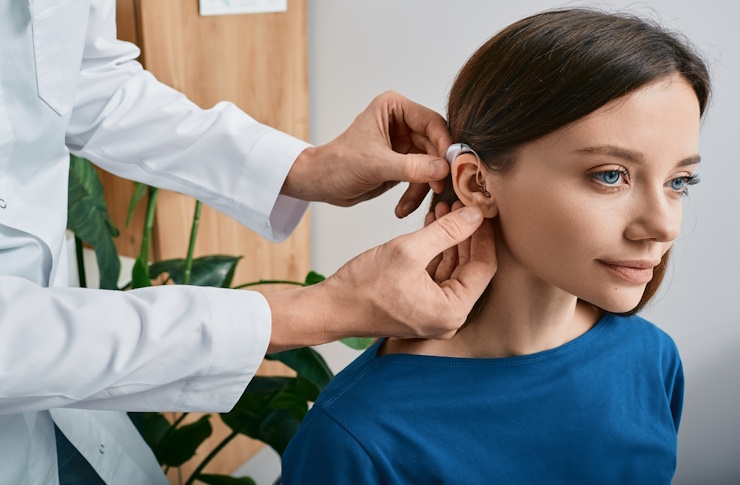
Professional removal: microsuction, clinical irrigation, and what to expect
Healthcare professionals use specialized techniques for safe, effective earwax removal. Microsuction employs a gentle vacuum system under microscopic guidance, providing precise control without introducing water into the ear canal. This method works well for patients with perforated eardrums or previous ear surgeries.
Clinical irrigation uses controlled water pressure and specialized equipment to flush out impacted wax safely. Professionals may also use curettes or forceps for direct removal under proper visualization. These procedures typically take 15-30 minutes and provide immediate relief.
| Service Type | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Ear Cleaning | General Practitioner | $50-150 |
| Microsuction | ENT Specialist | $100-300 |
| Clinical Irrigation | Audiologist | $75-200 |
| Emergency Removal | Urgent Care | $100-250 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Safety and aftercare: preventing damage, recurrence, and when to follow up
Proper aftercare prevents complications and reduces recurrence risk. Keep ears dry for 24-48 hours after professional removal, avoid swimming, and use earplugs during showers if recommended. Some temporary hearing changes or mild discomfort are normal immediately following removal.
Prevent future impaction by avoiding cotton swabs, managing underlying conditions like eczema that increase wax production, and scheduling regular check-ups if you’re prone to buildup. Never attempt removal if you have ear pain, discharge, or suspected perforation.
Seek immediate medical attention for severe pain, bleeding, sudden hearing loss, or signs of infection following any removal attempt. Regular monitoring helps maintain optimal ear health and prevents serious complications.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.